Oversea:+86-13790081902
In data centers, fans are the lifeline for maintaining the stable operation of servers and network equipment. Since servers generate a significant amount of heat, efficient heat dissipation is crucial to prevent overheating, performance degradation, and even system crashes. As experienced backward-curved centrifugal fan manufacturers, SunxFan integrates tailored fan solutions optimized for high-density airflows in modern IT environments.
In practical scenarios, fans such as EC forward-curved centrifugal blower are widely applied in:
Server cabinet internal cooling: Each server typically has built-in small fans (like axial fans or centrifugal fans) that directly cool heat-generating components such as CPUs and GPUs.
In-row or in-rack cooling units: These units deliver cold air directly to server cabinets and draw hot air away using internal fans. EC blower is commonly used here due to their energy efficiency and precise speed control advantages.
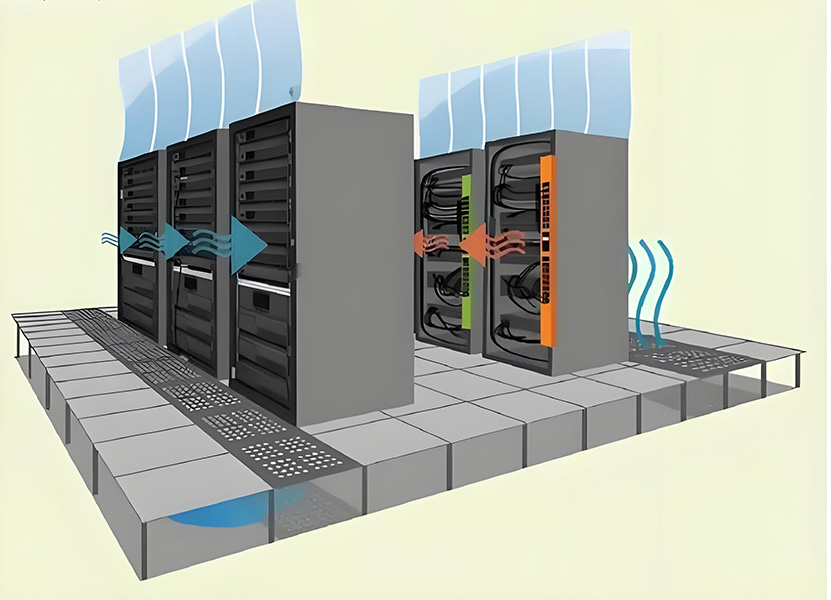
CRAC/CRAH (Computer Room Air Conditioner/Air Handler): Large data centers rely on these units for overall room temperature and humidity management. They typically integrate large-volume, high-static-pressure centrifugal fans to ensure effective cold air circulation.
Hot/cold aisle containment systems: Fans work in conjunction with aisle containment to ensure cold air flows only to equipment inlets, while hot air is expelled through dedicated pathways, enhancing cooling efficiency.
For fan selection, data centers prioritize:
High energy efficiency: To reduce operating costs, especially EC (electronically commutated) fans.
High reliability: To ensure 24/7 uninterrupted operation.
Low noise: To minimize noise pollution where possible.
High static pressure: To overcome airflow resistance and ensure effective heat dissipation.
In summary, data centers have extremely high demands for fans, as their performance directly impacts the data center's stability and energy consumption.
You can also check out locomotive cooling fan in our blog post.
Quick Links